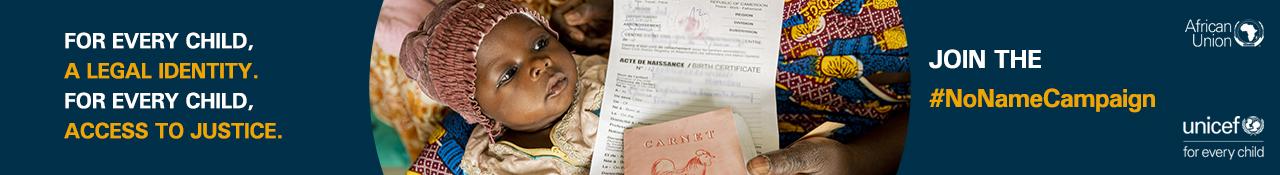
Department Resources
November 22, 2022
October 12, 2022
October 10, 2022
ASSEMBLY OF THE UNION
Thirty-First Ordinary Session
1 – 2 July 2018
Nouakchott, MAURITANIA
September 19, 2020
The African Union Commission (AUC) envisions “an integrated continent that is politically united based on the ideals of Pan Africanism an
June 24, 2020
Highlights of the cooperation with the GIZ-project “Support to the African Union on Migration and Displacement”
June 24, 2020
Violent extremism is a global issue.
September 22, 2024
September 05, 2024
February 10, 2022
Agenda 2063 is Africa’s development blueprint to achieve inclusive and sustainable socio-economic development over a 50-year period.
September 30, 2024
Climate change is arguably the greatest challenge facing humanity in the 21st century.
September 24, 2024